Popular wisdom says “everything is learned by comparison.” This principle also applies to welding equipment.
By placing a “classic” transformer next to an inverter apparatus, we see a significant difference in size and weight. You can’t carry a clumsy and heavy transformer “welder” in your hands. The inverter, on the contrary, can be thrown over your shoulder, get on a bicycle and go to the country.
Object transformer devices, operating as rectifiers or inverters, is very extensive and probably not fully exhausted in the article. In addition to the rectifier and rectifier circuits described above, there is still a whole series these devices with slightly different electrical diagrams. In addition, the switching process, which must be familiar to properly interpret and analyze the operation of the inverter, plays an important role in generating the receiver voltage and current. Therefore, all readers wishing to study or expand the above knowledge are referred to the literature and online resources below.
Compactness and minimal weight are two arguments in favor of choosing welding inverter for home. Besides these, the device has other advantages.
In order to make the best purchase, you need to have an idea of the structure and operating principle of inverter welding. This is where all its pros and cons are hidden.
Operating principle and main functions
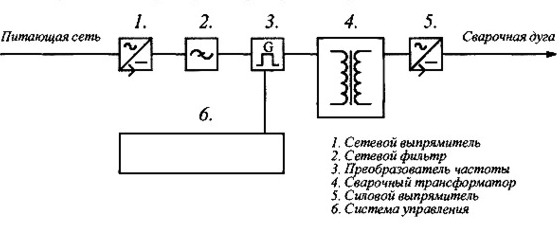
Anyone who didn't sleep in physics lessons knows that a welding transformer converts voltage and current. The 220 volts received at the input are reduced to 24-30 volts due to the phenomenon of magnetic induction. The current increases, reaching hundreds of amperes. This is enough to create a powerful and hot electric arc upon contact with metal. It melts the metal, joining it in the weld area.
The main distinguishing factor between different electromechanical methods is arc welding is a method of protecting welded materials from oxidation during welding and the type of welding material used. Typically, during welding, the combined metals form an anode and are connected to a positive power source. The welding electrode is the cathode, i.e. electron. Arc energy is generated by the flow of high-density electrons between the cathode and anode. The welding current depends on the settings of the welding machine, as well as on how the welding is performed.
Current adjustment is achieved by moving the electrode closer to and away from the weld material, but also depends on the current chiller settings. Sources of employee exposure are: - cables connecting the electrodes to the generator electrode; Welding inverters. Inverters can create currents up to tens of kHz - direct and alternating.
Due to the simplicity of the design, the transformer “welder” is inexpensive and practically “indestructible”. The welding inverter is much more complex than its transformer “ancestor”.
The mains current in it passes not one, but four stages of conversion:
- Straightening;
- Anti-aliasing filter;
- Conversion by inverter DC in high-frequency alternating (20-50 kHz);
- Reducing the voltage (70-90 V) while simultaneously increasing the current to 100-250A;
- Power rectification of current.
The electromagnetic field is generated during the welding process by the current flowing from the welding unit to the welding electrode through the cable that supplies it. Electric circuit covered by the welded components and, possibly, the welding table on which they are laid, and the return cable connecting them to the zero point of the welding machine. The electromagnetic field is located near the welding electrode, separated cables, electrode and return, welding table and welding machine body. Welding devices are usually operated manually.
Very often, welds are made with an electrode held in the hand, with wires running on the employee's body, and sometimes on the knee or shoulder. In this case, there is a very small distance from the employee’s body from above. Sources magnetic field lead to a relatively strong influence of the field on the employee’s body. Depending on the nature of the welds being made, they work in a variety of positions. When performing welding work on various structures, often very large in size, such as work in a shipyard or in construction, various positions of the worker's body and very different arrangement of cables are possible, including the described practical cases of tying work cables. Switching on the electrode or installing it in reels long cables.
For beginners, the most important three functions of the device are:
- Hot start (“Hot start”);
- Anti-stick (“Anti-Stick”);
- Forcing the welding arc (“Ark-Force”).
Anyone who has not yet learned to cook will suffer with the usual transformer welding, since the “cold” electrode does not want to melt the metal. All inverter welding machines have a hot start function, making it easier to get started. At this moment, the inverter automatically increases the current, creating a powerful “starting” arc.
In close proximity to welding electrodes and wires supplying them with magnetic fields of different frequencies of intermediate zone intensity values, as well as dangerous hazards, as determined in accordance with the provisions of the applicable regulations and limited access for people with pacemakers. The range of protection zones depends on the welding current and frequency. Inverter welding equipment does not produce electric fields with the intensity of protective zones. The level of exposure to the welding machine depends on the coverage of the protective zones and on the organization of the workplace and how the welding is carried out.
The anti-sticking function automatically reduces the operating current at the moment the electrode sticks. After it is torn off, the inverter restores the specified welding parameters.
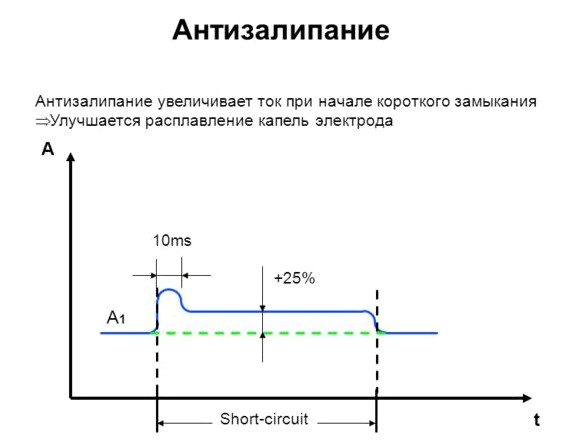
The electrode continuously melts during operation. The molten metal separates from it in the form of a drop, thereby shortening the arc length and causing sticking. At this moment, an inverter with the “Ark-Force” function briefly increases (boosts) the welding current, reducing the likelihood of electrode sticking. Setting this parameter (available in some models of welding inverters) allows you to obtain a “soft arc” with minimal metal spattering.
Random electromagnetic field hazards - 50 Hz magnetic field with induction above 100 µT and magnetostatic field with induction above 0.5 mT can interfere with electrical stimulators. - electromagnetic fields generated during welding can cause interference with control equipment operating near welding machines.
Recommended methods to effectively limit exposure - Move the worker as far as possible from power cables - Properly organize the work area and route welding cables to prevent direct worker contact with them.
In addition to facilitating the welding process, a good inverter welding machine is “omnivorous”. It works with constant and AC, excellent at welding cast iron and non-ferrous metals. They can also work on stainless steel. To do this, you will need a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a cylinder of inert gas (argon). The argon arc welding mode is designated by the abbreviation TIG.
Relatively weak source of electromagnetic field - rails or cables of medium voltage 15 kV - the main source of electric field in switchgear. Employee exposure characteristics. Employees do not constantly work at transformer stations. Workers' exposure to electromagnetic fields of 50 Hz occurs only when checking the operating conditions of equipment at stations and their maintenance, repairs and switches. These operations are performed in electromagnetic fields of various sizes.
The shock protection principle also ensures that exposure to strong electric fields that occur in the vicinity of medium voltage conductors and strong magnetic fields directly on low voltage conductors is limited. Work exposure to electric and magnetic fields can be assessed based on routine measurements and national occupational safety and health legislation. Our own research has shown that in most typical transformer stations, where workers may remain during normal transformer operation, only magnetic fields are present at levels in the safe and intermediate zones.

With a household inverter you can easily weld very thin metal using the “semi-automatic” mode. For this purpose, there is a special socket on the body of the device, to which a device that supplies welding wire is connected (purchased separately).
At distances greater than 1 m from low-voltage conductors, magnetic induction typically does not exceed 75 μT, which is considered acceptable for exposure to the general population. Magnetic induction, measured at a distance of 15 cm from low-voltage busbars, does not exceed several hundred µT. The location of workstations near transformer stations may cause people to question whether they are safe from exposure to electromagnetic fields generated by power equipment. These problems are exacerbated if noise in the room is caused by transformers, vibrations in the building, or poor picture quality on a computer monitor or TV.
In addition, to use the semi-automatic welding mode, you will need a carbon dioxide cylinder. There are semi-automatic inverters on sale (designated MIG/MAG), in which the feeder is mounted directly in the housing.
Basics of choosing a welding inverter for home use
Welding equipment is usually divided into three categories:
Based on our own research, the value of magnetic induction in rooms adjacent to transformer stations, depending on the conductivity of cables or current rails, can be close to 30 µT in the immediate vicinity of the walls. In most cases, the magnetic induction does not exceed a few µT and is many times below the occupational exposure limit. The impact of fields of such values may be considered negligible in a production environment, although it is technically and organizationally desirable to reduce it.
The electrical field is shielded through the walls of the building and in rooms adjacent to transformer stations, and its intensity does not increase compared to the values found in typical office or residential areas. Emergency Hazards - Possibility of Electrical Sting - Possibility of Electrical Shock.
- Industrial;
- Professional;
- Household.
Inverters differ significantly from each other in cost and operating cycle time. If you don’t need to weld metal for hours, then there is no point in buying an expensive professional model. We also note that the quality of the resulting seam practically does not depend on the “steepness” of the machine. Therefore, it is most reasonable to purchase a household appliance that can run continuously for 10-20 minutes, after which it needs to be given half an hour to cool down.
Preventative measures to reduce exposure - reducing the size of magnetic fields penetrating into adjacent rooms with stations can be achieved by keeping electrical components, cables and busbars close to each other, allowing mutual compensation of the magnetic field occurring around the power cables to perform different phases.
Other preventive measures - training on Electromagnetic hazards in the work environment -. The use of high-frequency switching power supplies in welding equipment has led to numerous improvements known for its non-industrial applications. By moving from frequency-frequency equipment to high-frequency switching converters, it was possible to increase the efficiency of devices and reduce their volume and weight. As a result, switching power supplies have been used in various types welding machines with metal and tungsten electrodes in noble, arc and resistive gases, as well as in plasma machines.
We also note that all household inverters intended for manual arc welding are designated by the abbreviation MMA, after which the manufacturer indicates the amount of operating current (MMA 200, MMA 250).
Technical Parameters
Input voltage range
Obviously, increasing the efficiency and reducing the size of power supplies, due to the complexity of the system compared to network devices, comes at a cost. The design of the welding machine source is more complex due to the nonlinearity of the welding arc. Therefore, the control circuit of the welding machine power supply must be more complex than that of conventional power supplies. Power supplies for welding machines stand out in addition to this high load current and high power. The welding current is designed for hundreds of amperes.
With an arc voltage of about 30 V, this means a power of many kilowatts. These requirements translate into high-voltage switching power supplies and enclosures that must meet increased thermal load requirements. A switching power supply for a welding machine usually consists of an input rectifier stage, an inverter, a high-frequency transformer and an output rectifier stage. His work is supported various functions controls such as pulse width modulation, gate control and soft start.
Deciding which inverter apparatus for welding it is better to buy, do not make a mistake by choosing a device designed for 220-230 Volts. It is necessary that in it technical specifications there was a range from 170 to 250V or the permissible voltage deviation was indicated within 10-15%. With this inverter you can confidently work both with insufficient and excess voltage in the household network.
The input diode circuit configuration depends on whether the system is powered by single or three-phase AC. If power factor correction is required, additional inverter circuits can be activated between the switching transistors and the rectifying diodes. The converter itself can be implemented as a full transistor circuit with four transistors or a half-bridge circuit with two transistors and two diodes. The latter simplifies control, but at the expense of efficiency.
The configuration of the output stage depends on the requirements of the specific welding equipment. Gas welding machines with gas protection require direct current. Others require constant current and constant voltage and constant current or pulse current. Depending on this, the circuit behind the rectifier diodes may consist of different components. When, for example, a welder requires direct current to weld steel or copper, it may be a gland. But when aluminum pulse is required for pulsed DC, a second inverter can be used instead of the gland.
Duration of switching on (DS)
It is indicated as a percentage and indicates the ratio of work time to the duration of the break. For example, a duty cycle value of 60% (optimal for a household inverter) tells us that after 10 minutes of operation at maximum load (at a temperature of + 20C), the device needs to be given 4 minutes to cool down. If the PV is exceeded, the thermal protection will operate and the device will turn off.
The semiconductor elements selected or designed for each section of the power supply must be optimized for different parameters. Input rectifiers must be surge-resistant and must have low conduction voltages to minimize conduction losses.
Designed to operate at frequencies up to 100 kHz, high-voltage transistors used in power levels must have low switching losses. They should be coupled with diodes to improve the best reverse charging characteristics. In other words, the recovery time should be as short as possible. The value of this parameter obviously depends on the switching frequency used. Thus, the operating conditions of these transistors determine the degree and "quality factor" required by the enhancement diodes.
Operating current regulation range
Determines the degree of versatility of the inverter. The wider it is, the more different jobs you can do (welding thin and thick metal, cutting). For most household tasks, a working current of 150-200A is sufficient.
Electrode diameter (from 1.4 to 6 mm)
Directly depends on the strength of the welding current. This parameter is always indicated in the technical specifications.
Let us give practical advice: it is better to purchase a device with a small margin: instead of a device designed for a 3 mm electrode, it is advisable to buy a device that can work with a “four” or “five”. This will make it possible to obtain a better quality seam when undervoltage when the efficiency of metal welding decreases.
Ventilation system
An important technical nuance is inverter ventilation. All inverter-type welding machines react painfully to dust, so tunnel ventilation technology was invented for professional models. For a household device that does not work in a construction site or workshop, this parameter less significant. However, the welding inverter must be disassembled periodically (at least 2 times a year), cleaning its insides from dust.
Temperature range
All electronic microprocessor devices (the inverter is no exception) do not like low temperatures (-15C and below). Take this point into account when purchasing and pay attention to the temperature operating conditions declared by the manufacturer. Optimal from -10 to +40C. The device should be stored in a warm room. The garage is not suitable for it. Here, frost and sudden temperature changes (condensation) can damage electronic board management.
The most sensitive and expensive component is the IGBT power module, which inverts the current (up to 30% of the cost of the device). It is not difficult to disable it: by overload as a result of a power surge or when quickly cutting thick metal with an electrode (the thermal protection does not have time to operate).
When choosing inverter welding, you should first of all be interested in user reviews. In them you can learn a lot of important and useful information about the quality of components of a particular brand, the availability of service and the level of professionalism of its employees.
Popular manufacturers and estimated prices
A welding inverter is a complex and expensive electronic device, so it is very important to find a reliable manufacturer. There are many problems here. Indeed, how to do right choice among dozens of brands and brands? How to buy an inexpensive welding machine that you don’t have to take for repairs after several days of work?
As we have already said, the best method is to learn from the mistakes of others. Before purchasing, read as many reviews as possible about the model you like. Slowly weigh the pros and cons, and only after that make a final conclusion. In addition to reviews, the quality of welding equipment can also be judged by its price. This point should be discussed in more detail.

In the category of expensive professional devices is the Finnish brand Kemppi. In 2014-2015, the cost of an inverter from this company (Minarc 150), which creates a welding current of 150A (4 mm electrode), starts at 27,000 rubles.

In the category of household appliances with good and predictable quality, the German brand Fubag (popular models: IN 163, IR 200), Italian Telwin (Telwin Force 165) and Blueweld, Chinese Brima (Brima TIG-180A), Foxveld ( Foxweld Master 202), Elitech AIS 160CA, Wester, Aurora, Svarog (ARC 205) and Kedr (MMA-220F). Estimated prices for the most popular devices of these brands range from 8 to 16 thousand rubles.


In the category of cheap devices up to 6,000 rubles, you can also find models from some of these companies, however, today their range is not so large and is limited mainly to inverters with a maximum welding current of 140-160A, not of the best quality.
2015-02-07 41 688Relatively recently, inverter welding machines appeared on the shelves. In addition to their compact size, a significant difference between household inverters is the light weight of the installation, which allows you to carry such a station in your hands. But the property that especially attracts the consumer is the ability to work from regular socket at 220V.
Models of inverter devices are constantly being improved, and additional functions are added. In this regard, a buyer who decides how to choose a welding inverter for his home may face an almost impossible task. What to look for when selecting suitable equipment among several dozen different models?
Operating principle of a household welding inverter
The best household welding inverters for home easily cope with the main task of converting voltage to ensure a stable arc. In fact, each of the devices, with varying efficiency, performs four important stages of transformation electric current. Namely:- Converting AC to DC.
- Transformation constant voltage back to AC, but with a high operating frequency.
- Reducing the frequency to the required parameters.
- Reverse rectification of already reduced high frequency voltage.
At first glance, it may seem that such constant transformations are unjustified, but as a result of their implementation, the productivity of the equipment significantly increases, and, equally important, the weight and dimensions are reduced.
For your home, it is better to choose an inverter welding machine that operates on 220V. A household installation will allow you to perform minor household work, and to connect it, you will only need to insert the plug of the device into one of the sockets.
How to choose an inverter semi-automatic welding machine for your home
There are six main criteria that you should pay attention to when choosing a reliable welding inverter for your home or garden. The quality of the installation will largely depend on how much the buyer is willing to spend. Even among economy class models, you can choose an acceptable option if you pay attention to the following:- For what purposes do you plan to purchase a household inverter welding machine? The thickness of the workpieces and pipes largely influences the selection of the electrode, the combustion of which, in turn, requires a certain power of the installation.
- Electrode diameter - this coefficient affects the ability to carry out work using the device. The diameter of the electrode is selected depending on the type of weld and the thickness of the metal being processed.
- Operating current - choosing a welding inverter for a summer house is much easier if you consider that a power of 30-40A is required per unit of electrode. Therefore, for a “C” electrode, an output current power of 90-120A will be required.
- The type of network being connected - the fact that the inverter will be used for a summer residence does not mean that it is necessary to limit the choice exclusively to equipment operating on a standard voltage of 220V. Some models are designed to operate on 380V, and they have a unit installed that adapts when connected to a generator. Household inverter-type welding machines for dachas, operating on 220V, may also have a similar device.
- Duration of continuous switching on or PV. This ratio is displayed as a percentage. The most common are devices with a duty cycle of 60-80%. In practice, this means that the equipment can operate for 6-8 minutes respectively. After this, the welding inverter will automatically turn on the idle mode.
- Rated current is an indicator that determines the load at which the device will not overheat. Some manufacturers indicate the maximum current instead of the rated current. Which is not entirely correct and does not allow us to make correct calculations.
How can these criteria in practice affect the choice of a household inverter welding machine for the home? For example, it is planned to process metal 3-4 mm thick with a “C” electrode, then it is easy to calculate that the operating power should be 120 A. But if the installation’s PV is 40-60%, then these calculations will be erroneous.
The fact is that in addition to calculations related to power, it is also necessary to take into account the margin for equipment overheating. In case of low duty cycle, about 30-50% of power should be added. For such work at home or in the country, you will need household inverter welding machines rated at 160-180A.
Which company to choose a household welding inverter
As already noted, inverter-type household semi-automatic welding machines may differ in quality, reliability and cost. The choice of manufacturer of these products significantly influences these criteria. We can conditionally divide all types of equipment according to this criterion into three main categories:- European concerns - they produce productive inverter welding, with additional systems helping to avoid typical difficulties during work: sticking of the electrode, overheating of the device, etc. Household devices from European manufacturers such as EWM, Telwin, etc. can cope with high loads and can be classified as semi-industrial installations. The pricing policy of the companies is such that on average you will have to pay for an inverter welding unit as for an industrial Chinese machine. But the high cost guarantees quality and long service life.
- Domestic manufacturer - optimal solution For your home, you will want to purchase an inverter semi-automatic welding machine made in Russia or Ukraine, especially if you plan to use the installation exclusively for domestic purposes. The quality is different from Svarog, Patona and others. It should be borne in mind that sometimes Chinese manufacturers disguise themselves as well-known Russian brands. Therefore, when purchasing all kinds of Tempos, Rhythms, etc., most likely, you are buying a Chinese fake, which begins to emit the smell of burning plastic at the slightest overheating.
- China - inverter-type semi-automatic home welding machine from Chinese manufacturer It's a risky business. The only thing that can be tempting about Chinese products is the low installation cost. If you plan to use the welding machine occasionally, you can choose something from the official factory in China. Reviews show that the Resanta model has good characteristics.
It is best to buy the model you like in stores that are official representatives of the manufacturers. This way you can avoid counterfeiting and purchase a truly high-quality inverter-type household welding machine.
Connecting the welding inverter to a household network
The inverter device is connected using a ready-made extension cord and an electrical plug. The difficulty is that some external power supply networks, especially in older houses, are not designed for such a load. But if the house was built according to modern GOSTs, then there should be no problems with the connection.Electrical networks designed for a power of 16A can satisfy the current needs of a household welding device. In addition, the operating principle of inverter household models reduces the number of overloads by electrical network Houses.
If the wiring is not designed for increased electricity consumption, then you can connect directly from the meter by connecting to the power cable terminals.
If connecting the welding inverter to the home network is not possible, the installation can be powered directly from the power line. To do this, you will need to obtain permission from your local energy sales office.
Selecting inverter welding for household needs should be based on the final cost of installation, the required performance of the device, the type of network being connected and the power source. All these criteria will help you choose the most suitable equipment for your garden.





